POSETTE 2025 is a wrap! 🎁 Thanks for joining the fun. Missed it? Watch all 42 talks online.
Why Citus?
- Parallelized
PerformanceThe Citus database distributes your Postgres tables or schemas across multiple nodes and parallelizes your queries and transactions. The combination of parallelism, keeping more data in memory, and higher I/O bandwidth often leads to dramatic speed ups. In this chart, we show a benchmark SQL query running ~40x faster with an 8-node Citus cluster vs. a single Postgres node.
Time to complete a SQL query, using a benchmark that measures analytical query performance. Run on ~100 GB of GitHub archive data in JSON format. All servers are Azure VMs with 16 vCPUs, 64 GB of memory, and network-attached disks with 7500 IOPS—running Postgres 13 and Citus 9.5, with default settings. - Distributed
ScaleCitus makes it possible to distribute your data, queries, and transactions across multiple nodes—by row or by schema. In addition, the architecture includes a distributed query planner and an adaptive query executor. You can shard on a single node, query from any node, and you can use the columnar feature to achieve compression ratios of 3x-10x or more. Citus is a 100% open source Postgres extension.
When querying a Citus cluster, most applications query the Citus coordinator as shown here. You can also query from any node (excluding schema changes, those still go to the coordinator.) The Citus node you connect to will transform the queries & route them to the correct shards. - Power of
PostgresCitus is an open source extension to Postgres (not a fork.) So when you use Citus, you’re still using Postgres under the covers, along with the Citus extension on top. To your application, running on a Citus distributed database is like running on top of a single Postgres node. And because Citus is an extension, it’s easy for us to keep Citus current with the latest Postgres releases—plus you get the performance benefits of horizontal scale, while still being able to leverage your familiar SQL toolset and your Postgres expertise.

Postgres, PostgreSQL, and the Slonik Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of the PostgreSQL Community Association of Canada, and used with their permission. - Simplified
ArchitectureBecause Citus distributes your data, parallelizes your queries, keeps more data in memory, and gives you higher I/O bandwidth—Citus can meet the demanding performance requirements of mixed OLTP and OLAP workloads. So you can simplify your architecture by using a single database for your app’s transactional and analytical workloads, even for data-intensive applications. Citus gives you more capabilities: you can now use both columnar and row-based tables in your Citus distributed database. And with Citus 12, you can now easily support microservices.
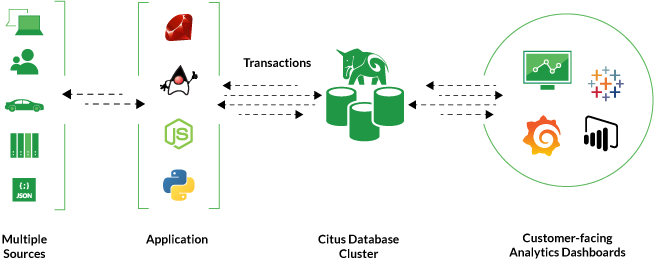
Diagram of a common use case for Citus: data-intensive applications that serve mixed transactional and analytical workloads. The transactional workload requires the robustness of a relational database like Postgres. And since the analytics dashboards are often customer-facing, they typically require low-latency query response times.
Learn Your Way: Read, Watch, or Do
Read the docs
Find out more about the Citus concepts, architecture, cluster management, APIs, use cases, & performance tuning.
Watch the videos
See how Citus scales out Postgres and parallelizes your workloads via these YouTube videos. Tip: turn on captions.
Try the tutorials
Learn how to use Citus by using sample data in these short tutorials. For time series data, check out the use case guide.
Try Citus Right Now
Citus Open Source
You can download and install Citus open source packages for Docker, Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, and Red Hat via these simple steps.
Citus on Azure
You can stand up a Citus cluster in minutes with the Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL managed service.
2 Ways to Shard Postgres with Citus
Using sharding and replication, the Citus extension distributes your data and queries across multiple nodes in a cluster, to give your app parallelism as well as more memory, compute, and disk.
Schema-based sharding: First introduced in Citus 12, schema-based sharding is easier to use since you don’t need a distribution key. Good for multi-tenant SaaS & microservices. Each tenant has a separate schema with its own set of tables, in the same database.
Row-based sharding: Row-based sharding is the traditional way Citus does sharding and is useful for all use cases, especially real-time analytics, time series, & IOT. The data from all tenants is in the same set of tables. Each table has a tenant ID column (or equivalent) which acts as the distribution column.

How Citus Works
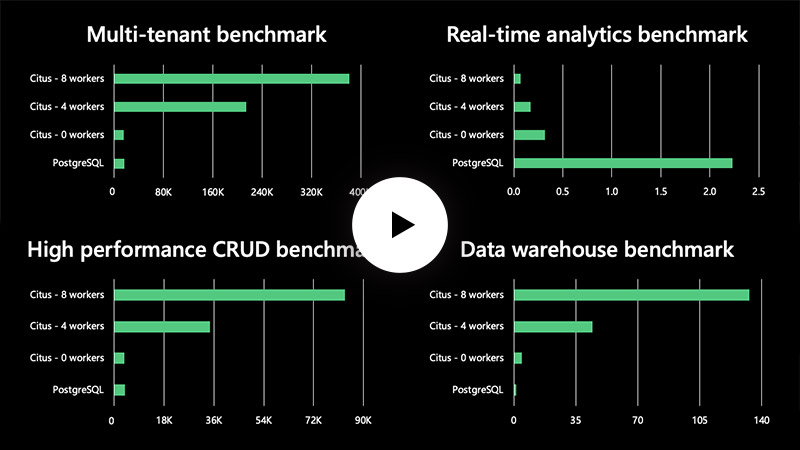
Learn how Citus works in this talk about Citus table types, the PostgreSQL extension APIs, the Citus query planner, and performance benchmarks comparing multi-node Citus clusters to a single node.
Citus Deep Dive
Data Modeling
Migration & Guides
Performance Tuning
What’s New in Citus?
Blog Post
Citus 13 blog post
Release Notes
Official release notes for Citus 13.0
Blog Post
Schema-based sharding comes to Postgres with Citus
Blog Post
Citus 12.1 blog post
Release Notes
Official release notes for Citus 12.1
Blog Post
How Citus supports the PostgreSQL MERGE command, as of Citus 12.0
Blog Post
Distributed PostgreSQL benchmarks using HammerDB, by GigaOM
Blog Post
Citus 12 blog post
Release Notes
Official release notes for Citus 12
Blog Post
Distributed Postgres goes full open source with Citus: why, what, & how
Open Source News
Open sourcing the Citus shard rebalancer
Blog Post
How to scale Postgres for time series data