POSETTE 2025 is a wrap! 🎁 Thanks for joining the fun. Missed it? Watch all 42 talks online.
Scale Out Without Sacrificing SQL (Keep Postgres, too)
Most SaaS applications are inherently relational. With sharding Citus gives you the ability to scale out your SaaS database with full SQL coverage, so you don’t have to give up the relational semantics you need, like joins, foreign key constraints, transactions, ACID, consistency. By scaling out, your app gets much bigger memory, compute, and disk footprint—ensuring performance even in the face of growth. And since Citus is an extension to Postgres, you can leverage all of your existing expertise—plus all the Postgres reliability, rich data types (think: JSON and PostGIS), Postgres extensions (our favorites include HyperLogLog), and ongoing innovation in the amazing Postgres open source community.

2 Ways to Shard Postgres with Citus
Citus offers 2 ways to shard Postgres—by schema or by row. Your app’s requirements will guide your choice. The biggest benefit of schema-based sharding is ease-of-use—no additional data-modeling steps are required, only a single setting change. Good for multi-tenant apps & microservices. On the other hand, row-based sharding allows you to more densely pack your tenants on nodes—plus cross-tenant queries are supported. Best for real-time analytics, time series, & IOT. A single application can use one set of tables when sharding by schema is appropriate and another set when sharding by row is best.

Shard Your SaaS Application by Schema
First introduced in Citus 12, schema-based sharding is easier to use since you don’t need a distribution key. Good for multi-tenant SaaS & microservices. Such applications serve many different tenants from a single deployment, often backed by a single database for ease-of-management and cost efficiency. Most queries done by these applications can be scoped to a single tenant, which makes the schema a natural shard key. You can shard your Citus database by creating a schema per tenant, as an alternative to distributing tables by a tenant ID column.

Shard Your Multi-Tenant Application by Row
For multi-tenant applications that keep their data in a set of shared tables, row-based sharding—the traditional method of sharding in Citus—is another choice. Row-based sharding allows for a very dense packing of tenants, resulting in efficient hardware use. It also makes cross-tenant queries trivial, which is important for a lot of dashboards/analytical use-cases.

Get an Elastic Database That Works With Rails & Django
So you want a database that can handle peak workloads and boatloads of concurrent users; act as a system of record and provide business analytics; offer high availability and provide elastic scale as your customer base triples in size. Check. The icing on the cake is for the database to integrate seamlessly with your frameworks like Rails, Django, Hibernate, and Sequelize. Because Citus is an extension to Postgres, we’ve been able to build on top of the robust, existing Postgres integrations and make it easy for multi tenant apps to use Citus: recent additions include an activerecord-multi-tenant gem for Ruby on Rails, and a Python django-multitenant library for Django. More to come.
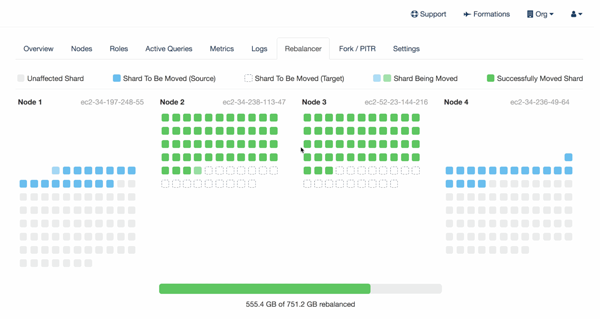
Shard by Tenant to Scale Out Your Multi-Tenant Application
While you may have a lot of data and your SaaS database may soon be too big for single-node Postgres, it’s likely that any given customer of yours can get the database performance they need from a single node. With our Citus extension to Postgres, the database is scaled out and yet data for each of your SaaS customers is
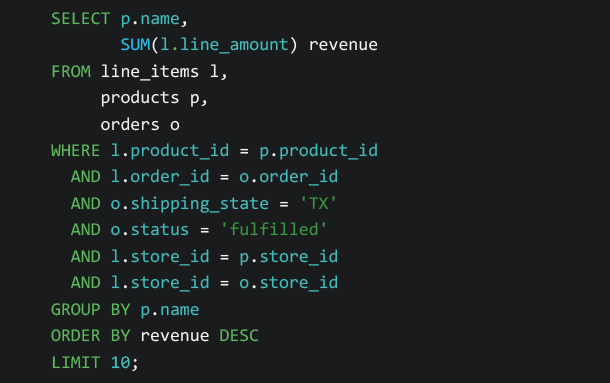
Analyze Activity with Powerful Cross-Shard Queries
As of Citus 10 you can run Citus on a single node, or on multiple worker nodes—with Postgres and Citus installed on each node in the cluster. If you’re running your app on Citus in the cloud and you have HA turned in Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL, then standby nodes will exist, too. Citus shards the database tables based on the distribution key, and then distributes shards across the worker nodes. The pièce de résistance: Because Citus can parallelize query fragments across multiple nodes in a cluster, you can run powerful cross-shard queries across all of your customer data quickly and easily.

Monitor Tenants
Find noisy neighbors in your cluster with CPU usage insights and query counts from citus_stat_tenants. Citus maintains a resource utilization snapshot for top N tenants you can use with Grafana to visualize congestion & locate roadblocks.



